A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals; for example, “5” is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents. [1]
We use numbers in our day to day life. They are often called numerals. Without numbers, we cannot do counting of things, date, time, money, etc. Sometimes these numbers are used for measurement and sometimes they are used for labelling. The properties of numbers make them capable of performing arithmetic operations on them. These numbers are expressed in numeric forms and also in words. [2]
Types of Numbers
The numbers can be classified into sets known as the number system. The different types of numbers in maths are: [2]
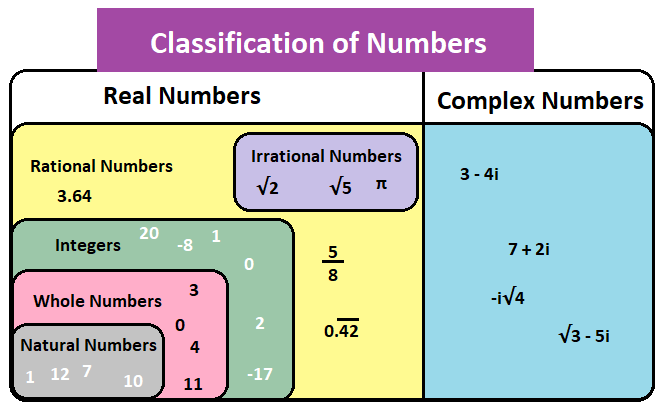
- Natural Numbers: Natural numbers are known as counting numbers that contain the positive integers from 1 to infinity. The set of natural numbers is denoted as ℕ and it includes ℕ = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ……….}
- Whole Numbers: Whole numbers are known as non-negative integers and it does not include any fractional or decimal part. It is denoted as 𝕎 and the set of whole numbers includes 𝕎 = {0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5, ……….}
- Every whole number is a rational number (ℚ) because every whole number can be expressed as a fraction.
- Integers: Integers are the set of all whole numbers (𝕎) but it includes a negative set of natural numbers (ℕ) also. ℤ represents integers and the set of integers are ℤ = { -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3}
- Real Numbers: All the positive and negative integers (ℤ), fractional and decimal numbers (ℚ) without imaginary numbers are called real numbers (ℝ). The set of real numbers can also be divided into
- Rational Numbers: Any number that can be written as a ratio of one number over another number is written as rational numbers. This means that any number that can be written in the form of p/q. The symbol ℚ represents the rational number.
- Irrational Numbers: The number that cannot be expressed as the ratio of one over another is known as irrational numbers and it is represented by the symbol ℙ.
- Complex Numbers: The number that can be written in the form of a + bi where “a and b” are real numbers and i is an imaginary number is known as complex numbers ℂ.
- Imaginary Numbers: The imaginary numbers are the complex numbers that can be written in the form of the product of a real number and the imaginary unit i.
References
[1] “Number – Wikipedia”. 2023. en.wikipedia.org. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Number.
[2] “Numbers – Definition, Types Of Numbers, Charts, Properties, Examples”. 2023. BYJUs. https://byjus.com/maths/numbers/.
The featured image on this page is from the YouTube video Types of Numbers.
