Contents
- Fractions
- Fractions Are Division
- Difference Between Proper Fraction and Improper Fraction
- Proper Fractions
- Improper Fractions
- Mixed Number (Mixed Fraction)
- Converting Fractions to Decimals
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions
- Multiplying Fractions
- Dividing Fractions
- Comparing Fractions by Cross Multiply
- References
- Additional Reading
- Videos
Fractions
In Mathematics, fractions are defined as the parts of a whole. The whole can be an object or a group of objects. In real life, when we cut a piece of cake from the whole of it, then the portion is the fraction of the cake. A fraction is a word that is originated from Latin. In Latin, “fractus” means “broken”. In ancient times, the fraction was represented using words. Later, it was introduced in numerical form.
The fraction is also termed as a portion or section of any quantity. It is denoted by using ‘/’ symbol, such as a/b. For example, in 2/4 is a fraction where the upper part denotes the numerator and the lower part is the denominator. In this article, we are going to learn the definition of fractions in maths, types of fractions, conversion from fractions to decimals, and many solved examples with complete explanation. [1]
Fractions Are Division
k = constant (of proportionality)
Difference Between Proper Fraction and Improper Fraction
The difference between proper fractions and improper fractions is that they are opposite in regards to:
- Their relation to 1.
- The value of the numerator and denominator.
Relation to 1
A major property which defines a proper and improper fraction is its relation to 1. Proper fractions can only ever be smaller than 1. For example 3/9, 12/45, and 70/190. An improper fraction, however, will always be greater than 1 and can be turned into a mixed number.
Proper Fractions
A fraction in which the numerator value is always less than the denominator value is known as a proper fraction. For example, 18/25, 19/45, 62/78, 1/6, 1/9, are proper fractions. A fraction consists of two parts, the numerator, and the denominator, and various types of fractions are identified on the basis of these two values. The two primary fractions which are distinguished on this criterion are proper and improper fractions. [2]
Improper Fractions
A fraction whose numerator is greater than or larger than the denominator is defined as an improper fraction such as 7/3 and 12/5. Improper fractions are easier to solve using addition and subtraction compared to the type of fractions such as mixed fractions. [3]
Converting Improper Fractions to a Mixed Number
To convert an improper fraction to a mixed number, we need to divide the numerator by the denominator and then find out the remainder and the quotient. Now, the quotient becomes the whole number of the resultant mixed fraction, the remainder becomes the numerator part of the mixed fraction and the denominator part remains the same. [6]
Example: Convert the improper fraction into a mixed number: 7/3
Solution: On dividing 7 by 3, we get 2 as the quotient and 1 as the remainder. Thus, 7/3 will be written as 2 1/3 as a mixed number.

Mixed Number (Mixed Fraction)
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. Mixed numbers are also known as mixed fractions and they help us to understand a quantity in a simpler way. Mixed numbers consist of a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, 2 1/4 is a mixed number in which 2 is the whole number part and 1/4 is the proper fraction. It should be noted that mixed numbers can be added, subtracted, multiplied, and divided easily once they are converted to an improper fraction. [4]
Converting a Mixed Number to an Improper Fractions
Let us understand the method of converting a mixed number to an improper fraction with the help of an example. Let us convert the mixed fraction 7 1/5 to an improper traction using the following steps: [7]
- Step 1: Multiply the denominator with the whole number part. Here, 5 × 7 = 35.
- Step 2: Add the numerator to the product obtained in step 1. So, we get, 35 + 1= 36.
- Step 3: Write the value obtained in step 2 over the denominator. This will be the new numerator while the denominator will remain the same. So, 7 1/5 = 36/5.
Converting Fractions to Decimals
When a number is present in a fraction form i.e., p/q, we use the long division method to convert it into a decimal form. In such a case we divide the numerator by the denominator. Let us understand the steps involved in fraction to decimal conversion by the long division method with the help of an example. [5]
Convert 4/19 to decimal.
- Step 1: In the given fraction 4/19, consider the numerator 4 as a dividend and the denominator 19 as the divisor. In this case, the denominator > numerator.
- Step 2: We have to make the dividend digit (4) greater than the numerator digit (19) by placing 0 next to 4 and to the quotient respectively. Now we have 40 as a new dividend. (40>19)
- Step 3: In the quotient part, it is important to insert decimal (.) after 0 and start the division.
- Step 4: Multiply 19 with a number so that the product is less than or equal to 40. We know that 19 times 2 is 38. The digit that appeared in the quotient is 2, and the remainder left is 2. After introducing decimal in the quotient we can introduce one 0 at each step of division.
- Step 5: Now the new dividend is 20. Multiply 19 with a number so that the product is less than or equal to 20. 19 times 1 is 19. Now the new digit in the quotient is 1 which makes it 0.21, and the remainder is 1.
- Step 6: Repeat the steps till we get 0 as the remainder or at least three decimal places in the quotient.
Try to read out the steps with the image given below for having a better understanding of converting fractions to decimals. [5]

Adding and Subtracting Fractions
Addition and subtraction of fractions is done using similar rules in which the denominators are checked before the addition or subtraction starts. After the denominators are checked, we can add or subtract the given fractions accordingly. The denominators are checked in the following way. [8]
- If the denominators of the given fractions are the same, we add or subtract only the numerators and we retain the denominator.
- If the denominators are different, we convert the fractions to like fractions so that the denominators become the same, and then we add or subtract, whatever is required.
Adding and Subtracting Fractions Using Cross Multiplication
Cross multiply can be defined as the process of multiplying the numerator of the first fraction on one side of the equals to symbol, with the denominator of the second fraction on the other side of the equals to symbol. Similarly, the denominator of the first fraction is multiplied by the numerator of the second fraction. Cross multiply is also called cross-multiplication or butterfly method. When we want to determine one or more variables in a fraction, we use the method of cross multiply. Fractions can also be compared by using the process of cross multiply.
When two fractions p/q and r/t are multiplied by each other, the process is termed cross multiply or cross-multiplication method. For example p/q and r/t are two fractions and to cross multiply we multiply p × t and q × r as shown in the image below. [9]

Here are the steps of adding fractions using the butterfly method:
- Multiply the numerators and denominators diagonally.
- Add the product of the diagonal pairs of numerators and denominators together. This creates the new numerator.
- Multiply the denominators by each other. This creates the new denominator.
- Simplify the fraction if possible.

Multiplying Fractions
The multiplication of fractions is not like the addition or subtraction of fractions, where the denominator should be the same. Here, any two fractions with different denominators can easily be multiplied. The only thing to be kept in mind is that the fractions should not be in the mixed form, they should either be proper fractions or improper fractions. Let us learn how to multiply fractions through the following steps: [10]
- Step 1: Multiply the numerators.
- Step 2: Multiply the denominators.
- Step 3: Reduce the resultant fraction to its lowest terms.
Dividing Fractions
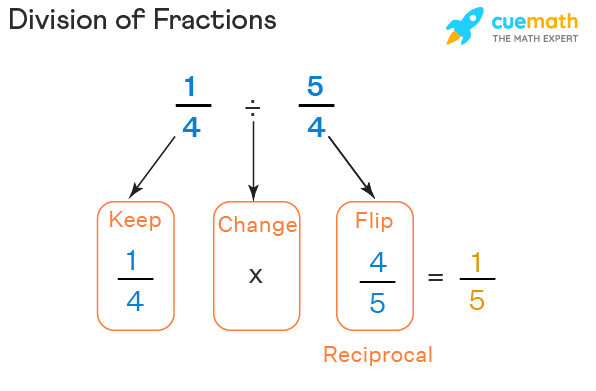
We know that division is a method of sharing equally and putting into equal groups. We divide a whole number by the divisor to get the quotient. Now, when we do division of a fraction by another fraction, it is the same as multiplying the fraction by the reciprocal of the second fraction. The reciprocal of a fraction is a simple way of interchanging the fraction’s numerator and denominator. Observe the following figure to learn a simple rule of dividing fractions. [11]
| Note |
|---|
| See K-12 – Division for additional information on dividing fractions. |
Comparing Fractions by Cross Multiply
Cross multiply is used in both like and unlike fractions. When a fraction is unlike i.e. when the denominators of two fractions are not similar while using the process of cross multiplication we not only multiply the numerators to the denominators but we also multiply the denominators. For example, in the image below when we cross multiply 3 × 4 and 2 × 5 we get 12 and 10 respectively. 12 and 10 are the numerators of the 3/2 and 5/4. To make the denominator as common we multiply both the denominators as well 2 × 4 = 8. Hence the new fractions with the same denominators will be 12/8 and 10/8. Since 12 is a greater numerator, 12/8 > 10/8. Therefore, 3/2 > 5/4. [9]

References
[1] “Fractions – Definition, Types, Properties and Examples.” 2022. BYJUS. BYJU’S. July 5. https://byjus.com/maths/fractions/.
[2] “Proper Fraction – Definition, Difference, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/proper-fraction/.
[3] “Improper Fractions – Definition, Conversion, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/improper-fractions/.
[4] “Mixed Numbers – Definition, Examples, FAQs.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/mixed-numbers/.
[5] “Convert Fraction to Decimal – Chart, Methods, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/fraction-to-decimal/.
[6] “Improper Fraction to Mixed Number- Conversion, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/improper-fraction-to-mixed-number/.
[7] “Mixed Number to Improper Fraction – Conversion, Meaning, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/mixed-number-to-improper-fraction/.
[8] “Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: Adding and Subtracting Fractions.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/addition-and-subtraction-of-fractions/.
[9] “Cross Multiply – Definition, Steps, Comparing Fractions & Ratios, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/cross-multiply/.
[10] “Multiplying Fractions: Multiplication of Fractions: How to Multiply Fractions?” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/multiplying-fractions/.
[11] “Division of Fractions – Steps, Method, Examples.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/division-of-fractions/.
Additional Reading
“Adding Fractions With Unlike Denominators – Adding Unlike Fractions.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/adding-fractions-with-unlike-denominators/.
⭐ Blázquez, Víctor Monterreal. 2023. FRACTIONS. Accessed November 6. http://www.mathspadilla.com/2ESO/Unit3-Fractions/index.html.
“Fractions”. 2023. Accessed November 25. mathsisfun.com. https://www.mathsisfun.com/fractions.html.
⭐ “Fractions – Definition, Fraction Examples, What Is a Fraction?” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed November 25. https://www.cuemath.com/numbers/fractions/.
“Introducing Fractions as Division Is an Effective Way to Teach the Concept.” 2023. Math Blog for Differentiation. Accessed November 7. https://happynumbers.com/blog/Introducing-fractions-as-division-is-an-effective-way-to-teach-the-concept/.
Proper and Improper Fractions. 2023. content.nroc.org. Accessed December 29. https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalMath/COURSE_TEXT_RESOURCE/U02_L1_T2_text_final.html.
Mathematicians use three categories to describe fractions: proper, improper, and mixed. Fractions that are greater than 0 but less than 1 are called proper fractions. In proper fractions, the numerator is less than the denominator. When a fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to the denominator, the fraction is an improper fraction. An improper fraction is always 1 or greater than 1. And, finally, a mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction.
“Subtracting Fractions with Unlike Denominators – Formula, Examples, Steps.” 2023. CUEMATH. Accessed December 29. https://www.cuemath.com/algebra/subtracting-fractions-with-unlike-denominators/.
“Types of Fractions (Proper Fraction, Improper Fraction and Mixed Fraction).” 2020. BYJUS. BYJU’S. December 14. https://byjus.com/maths/types-of-fraction/.
Videos
Based on numerator & denominator there are different types of fractions in math. Three major types are defined for a single fraction and the other types determine the comparison between two or more fractions. let’s talk about different kinds of fractions.
This video explains a great hack, short cut when adding and subtracting fractions.
⭐ I suggest that you read the entire reference. Other references can be read in their entirety but I leave that up to you.
The featured image on this page is from the mathspadilla.com website.
