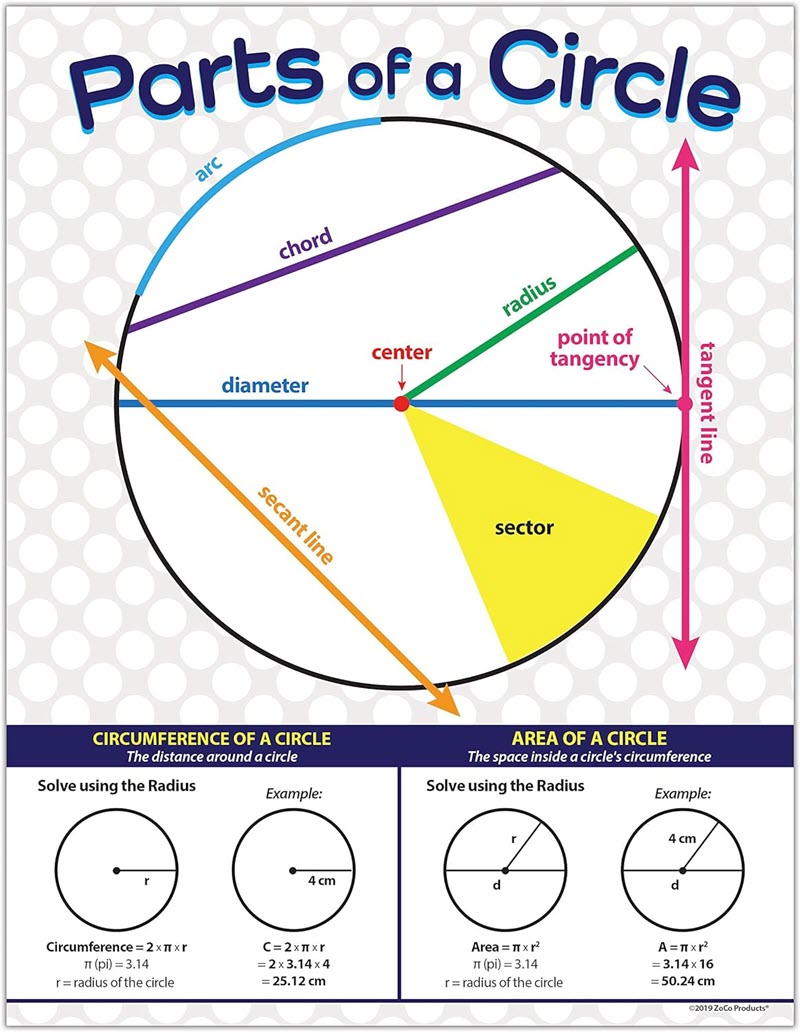
A Circle is a 2-dimensional figure. It is a closed figure in which boundary is equidistant from the center and distance from the center to the boundary is called radius and it remains the same throughout the figure. [1]

C is the center of circle. Perimeter of a circle is called circumference.
Important properties of a circle:
- Area of circle = π * r * r
- Perimeter of circle = 2 * π * r
or π * diameter - diameter = 2 * radius
General Equation of a Circle
The equation of the form x2 + y2 + dx + ey + f = 0 comes from the concept of conic sections
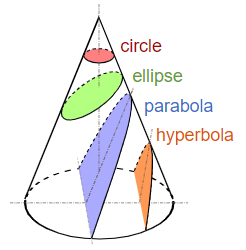
Conic is a plane algebraic curve of degree 2. It is a set of points whose coordinates satisfy a quadratic equation in two variables of the form
Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
Here A, B, C, D and E are constants
The conic sections described by this equation can be classified based on the value B2–4AC, called as the discriminant.
B2–4AC < 0 represents ellipse. Further, if A = C and B = 0, then the conic is a circle, which is a special case of ellipse.
We write,
Ax2 + (0)xy + Ay2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
Ax2 + Ay2 + Dx + Ey + F = 0
Divide by A,
x2 + y2 + (Dx)/A + (Ey)/A + FA = 0
This comparable to the given equation,
x2 + y2 + dx + ey + f = 0
where,
D/A = d, E/A =e, F/A = f [2]
When you say “derivation of the general equation of a circle” I assume you mean explicitly “how do we form or make the equation of a circle with a specific centre and radius”.
I ask this because many people mix up the words “derive” and “differentiate” .
“Derive” really means to make something but “differentiate” means to find the “gradient” or “derivative”.
Let’s do a specific example…
Suppose we want to derive (make) the equation of a circle with a radius is 3 units and the centre is at (6, 4)
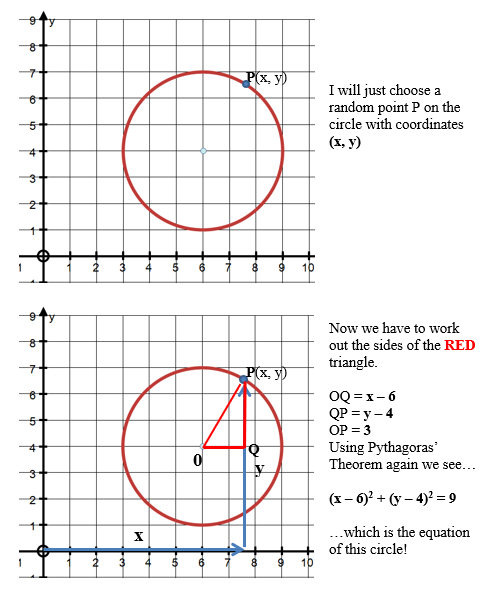
If we expand the equation.
(x – 6)2 + (y – 4)2 = 9
we get …
x2 – 12x + 36 + y2 – 8y + 16 = 9
Simplifying …
x2 – 12x + y2 – 8y + 43 = 0
Rearrangmg …
x2 + y2 – 12x – 8y + 43 = 0
which is of the required form …
x2 + y2 + dx + ey + f = 0 [3]
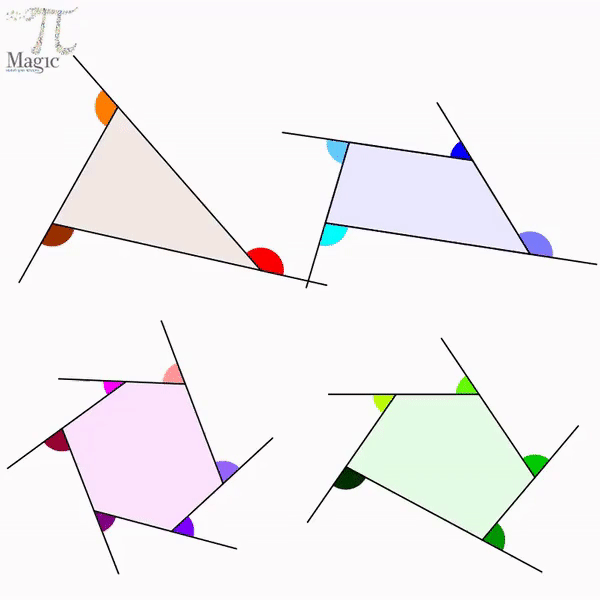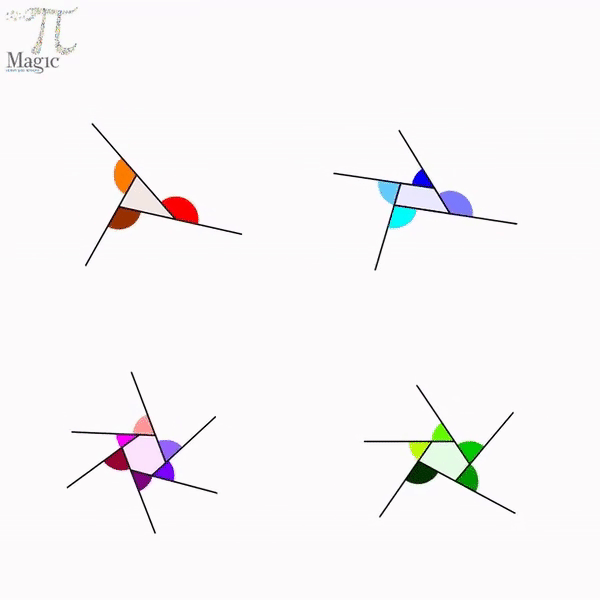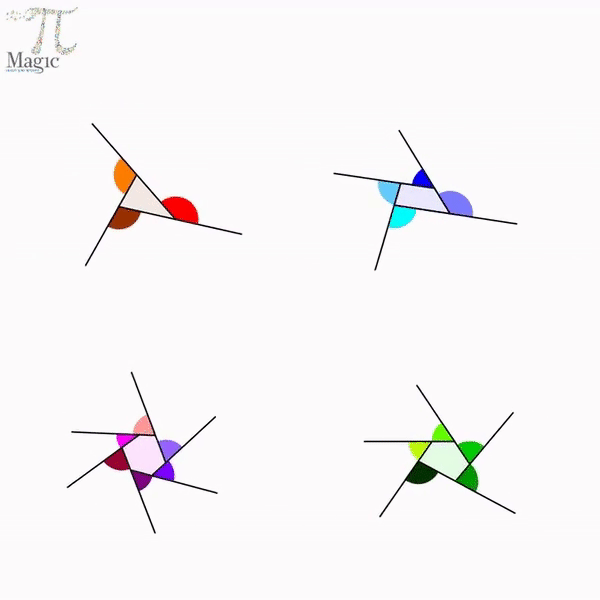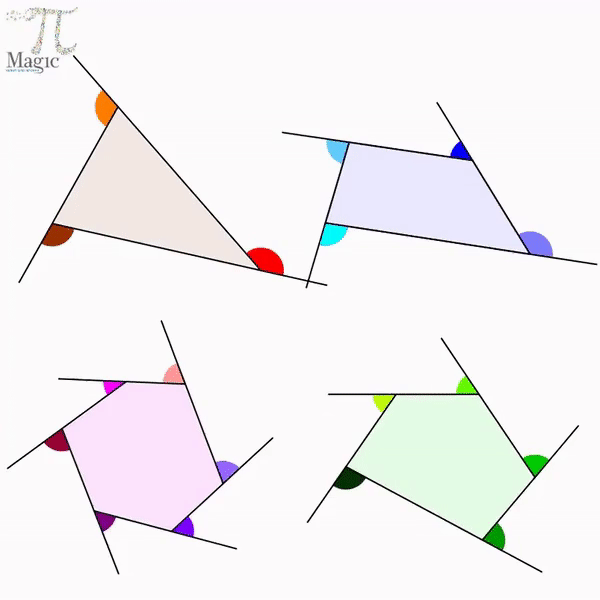
Sum of the Exterior Angles of a Polygon
If a polygon is a convex polygon, then the sum of its exterior angles (one at each vertex) is equal to 360 degrees.
Let us say you start travelling from the vertex at angle 1. You go in a clockwise direction, make turns through angles 2, 3, 4 and 5 and come back to the same vertex. You covered the entire perimeter of the polygon and in fact, made one complete turn in the process. One complete turn is equal to 360 degrees. Thus, it can be said that ∠1, ∠2, ∠3, ∠4 and ∠5 sum up to 360 degrees. [4]
References
[1] “GRE Geometry: Circles.” 2021. GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. October 24. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/gre-geometry-circles/.
[2] Hebbar, Pradeep. “Hello! Can you help me find where the derivation of the general equation of a circle x^2+y^2+dx+ey+f=0 come from?”. Quora. 2023. Accessed November 23. https://qr.ae/pKMNdu.
[3] Lloyd, Philip. “Hello! Can you help me find where the derivation of the general equation of a circle x^2+y^2+dx+ey+f=0 come from?”. 2023. Quora. Accessed November 23. https://qr.ae/pKMGGO.
[4] “Exterior Angles of a Polygon – Definition, Theorem and Examples.” 2022. BYJUS. BYJU’S. May 4. https://byjus.com/maths/exterior-angles-of-polygon/.
Additional Reading
⭐ “Circles.” 2023. Brilliant Math & Science Wiki. Accessed November 23. https://brilliant.org/wiki/circles/.
⭐ “Circle Geometry Properties.” 2023. Brilliant Math & Science Wiki. Accessed November 21. https://brilliant.org/wiki/circle-geometry-properties/.
“Sum of Exterior Angles of Triangle – Definition, Formula, Proof.” 2023. Cuemath. Accessed November 23. https://www.cuemath.com/geometry/sum-of-exterior-angles-of-triangle/.
Videos
⭐ I suggest that you read the entire reference. Other references can be read in their entirety but I leave that up to you.
The featured image on this page is from the Circle Geometry Properties page on the Brilliant Math & Science Wiki website.