Definition
“In complex analysis, Euler’s formula provides a fundamental bridge between the exponential function and the trigonometric functions. For complex numbers x, Euler’s formula says that
eix = cosx + isinx
In addition to its role as a fundamental mathematical result, Euler’s formula has numerous applications in physics and engineering.” [1]
Who
Euler’s formula exists in two main forms:
- For Complex Analysis (Euler’s Identity):
- Formula: eix = cos(x) + i * sin(x)
- Applications:
- Signal Processing: Decomposing complex signals into their frequency components, as in the Fourier Transform.
- Electrical Engineering and Signal Processing : Euler’s formula is essential for analysing AC circuits and signal processing. The rotation of complex numbers on the unit circle models oscillations, waveforms, and resonant frequencies.
- Quantum Mechanics : Complex numbers are central to quantum mechanics, where wave functions represent the probabilities of particles. Euler’s identity plays a fundamental role in understanding these wave-like behaviors.
- Physics: Modeling wave analysis, harmonic motion, and quantum mechanics, where it represents wave functions.
- Differential Equations : In calculus, Euler’s formula simplifies solutions to differential equations that involve complex numbers. This is vital in physics, engineering, and finance, allowing for the solution of problems related to oscillations, waves, and growth.
- Computer Graphics & Vision: Handling rotations and transformations in 3D space.
- Aerodynamics: Modeling air behavior around aircraft and objects. Euler’s equations are used to analyze and predict airflow patterns, allowing engineers to design efficient airfoils and optimize aircraft performance.
- Hydrodynamics: Analyzing water flow in rivers, oceans, and other environments. Euler’s equations are used to model the behavior of water and other liquids, helping to understand phenomena like ocean currents and tidal waves.
- For Polyhedra (Euler’s Characteristic):
- Formula: F+V−E=2
- Explanation: For any non-self-intersecting polyhedron, the sum of its faces (F) and vertices (V) minus its edges (E) is always equal to 2.
- Platonic Solids: There are 5 platonic solids for which Euler’s formula can be proved. They are cube, tetrahedron, octahedron, dodecahedron, and icosahedron.
- Applications:
- Geometry & Topology: Analyzing the structure of polyhedra and classifying them, as in the proof that there are exactly 5 regular polyhedra.
- Graph Theory: Studying planar graphs and relationships between vertices, edges, and faces.
Let’s verify Euler’s formula on complex polyhedra which serve as Euler’s formula examples.

Euler’s formula provides a way to link seemingly disparate mathematical concepts, enabling easier manipulation of complex systems and simplifying problem-solving across various disciplines.
What
Euler’s identity is more than just an equation — it is a bridge between vastly different realms of mathematics and science. Its simplicity and elegance have inspired generations of mathematicians, scientists, and engineers, proving that profound truths often lie in the most compact expressions. Whether describing the quantum world, analyzing waves, or processing signals, Euler’s formula continues to be a beacon of mathematical beauty and utility. [2]
Euler’s formula was given by Leonhard Euler, a Swiss mathematician. There are two types of Euler’s formulas: [3]
- For complex analysis: It is a key formula used to solve complex exponential functions. Euler’s formula is also sometimes known as Euler’s identity. It is used to establish the relationship between trigonometric functions and complex exponential functions.
- For polyhedra: For any polyhedron that does not self-intersect, the number of faces, vertices, and edges is related in a particular way, and that is given by Euler’s formula or also known as Euler’s characteristic.
At its heart, Euler’s Formula establishes a deep connection: [4]
- Exponential Growth and Oscillation: Normally, exponential functions invoke images of rapid growth. However, when an imaginary number is used as the exponent, the result is oscillatory behavior characterized by sine and cosine functions.
- Complex Numbers: Euler’s Formula illuminates the structure of complex numbers in a concise manner, expressing any complex number in its polar form.
Derived by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler in the 18th century, this formula was initially discovered as an identity relating power series expansions of exponential functions, sines, and cosines. Euler’s insights have since revolutionized many mathematical disciplines, showcasing the underlying unity of different branches of mathematics. [4]
Why
The following are two different Euler’s formulas used in different contexts.
- Euler’s formula for complex analysis: eix = cos x + isin x
- Euler’s formula for polyhedra: faces + vertices – edges = 2
Let us learn each of these formulas in detail. [3]
One of the uses of Euler’s identity is in removing trigonometric functions from equations. From it you can deduce expressions for sin, tan, cos, etc., in terms of their angles and e.
– Alfred Dominic Vella
“Euler’s formula gives us another way to describe motion in a circle. But we could already do that with sine and cosine — what’s so special?
It’s all about perspective. Sine and cosine describe motion in terms of a grid, plotting out horizontal and vertical coordinates.
Euler’s formula uses polar coordinates — what’s your angle and distance? Again, it’s two ways to describe motion:
- Grid system: Go 3 units east and 4 units north
- Polar coordinates: Go 5 units at an angle of 53.13 degrees
Depending on the problem, polar or rectangular coordinates are more useful. Euler’s formula lets us convert between the two to use the best tool for the job. Also, because eix can be converted to sine and cosine, we can rewrite formulas in trig as variations on e, which comes in very handy (no need to memorize sin(a+b), you can derive it — more another day). And it’s beautiful that every number, real or complex, is a variation of e.
But utility, schmutility: the most important result is the realization that baffling equations can become intuitive with the right analogies. Don’t let beautiful equations like Euler’s formula remain a magic spell — build on the analogies you know to see the insights inside the equation.” [5]
NOTES
Euler’s formula is a profoundly beautiful equation that says that the complex numbers, under exponentiation, don’t grow without limit but instead travel around a circle.
This single simple equation relates five of the most important numbers in mathematics: e, i, π, 0 and 1. Euler’s formula unites ideas across different fields of mathematics, showing that even the “imaginary” can have real meaning and application.
Euler’s identity combines five of the most important numbers in mathematics in a single, elegant equation:
- e : Euler’s number, the base of natural logarithms, fundamental in calculus.
- i : the imaginary unit, which introduces the concept of complex numbers.
- π : the famous constant that represents the ratio of a circle’s circumference to its diameter.
- 1: the multiplicative identity, essential in defining unity and structure in mathematics.
- 0 : the additive identity, representing nothingness, or a null quantity.
In one concise expression, Euler’s identity brings together these constants, each representing a different realm of mathematics: algebra, geometry, analysis, and arithmetic. Mathematicians have long admired Euler’s identity for its simplicity and elegance, seeing it as a kind of universal key that links disparate areas of mathematics. [7]
See Theoretical Knowledge Vs Practical Application.
How
It was around 1740, and mathematicians were interested in imaginary numbers. Leonhard Euler was enjoying himself one day, playing with imaginary numbers, and he took the well known Taylor Series, and he put i into it.
Because i2 = −1, it simplified.
If you group all the i terms at the end, the two groups are actually the Taylor Series for cosine and sine. And so it simplifies to:
eix = cos x + i sin x
QED [6]
Many of the References and Additional Reading websites and Videos will assist you with understanding and applying Euler’s Formula.
As some professors say: “It is intuitively obvious to even the most casual observer.“
References
[1] “Euler’s Formula: Brilliant Math & Science Wiki.” 2025. Brilliant. Accessed June 10. https://brilliant.org/wiki/eulers-formula/.
[2] Goyal, Shashank. 2024. “Exploring the Beauty of Euler’s Identity.” Medium. Medium. December 26. https://shashank-goyal-blogs.medium.com/exploring-the-beauty-of-eulers-identity-7a42805520dd.
[3] “Euler’s Formula – Complex Numbers, Polyhedra, Euler’s Identity.” 2025. CUEMATH. Accessed June 10. https://www.cuemath.com/eulers-formula/.
[4] Lee, Sarah. 2025. “Mastering Euler’s Formula Fundamentals.” Number Analytics // Super Easy Data Analysis Tool for Research. Accessed June 10. https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/ultimate-euler-formula-guide.
[5] “Intuitive Understanding Of Euler’s Formula.” 2025. BetterExplained. Accessed June 10. https://betterexplained.com/articles/intuitive-understanding-of-eulers-formula/.
[6] “Euler’s Formula for Complex Numbers.” 2025. Math Is Fun Advanced. Accessed June 10. https://www.mathsisfun.com/algebra/eulers-formula.html.
[7] ⭐ “The Magic of Euler’s Formula: Why This Is Considered the Most Beautiful Equation.” 2024. Medium. Medium. November 12. https://medium.com/@Mathfellow/the-magic-of-eulers-formula-why-this-is-considered-the-most-beautiful-equation-53a5c3b60ba2. [Medium Member-only Story]
Additional Reading
⭐ “Euler’s Formula: A Complete Guide.” 2022. Math Vault. May 18. https://mathvault.ca/euler-formula/.
⭐ McGeer, Rick. “Isn’t the Equation x2 + 1 = 0 Impossible?” 2025. Quora. Accessed June 10. https://qr.ae/pAVA91.
⭐ Toth, Viktor. “Isn’t the Equation x2 + 1 = 0 Impossible?” 2025. Quora. Accessed June 10. https://qr.ae/pA41cM.
“Euler’s Formula.” 2025. Math Wiki. Fandom, Inc. Accessed June 10. https://math.fandom.com/wiki/Euler%27s_formula.
One of the most important identities in all of mathematics, Euler’s formula relates complex numbers, the trigonometric functions, and exponentiation with Euler’s number as a base.
In the world of complex numbers, as we integrate trigonometric expressions, we will likely encounter the so-called Euler’s formula.
Named after the legendary mathematician Leonhard Euler, this powerful equation deserves a closer examination — in order for us to use it to its full potential.
We will take a look at how Euler’s formula allows us to express complex numbers as exponentials, and explore the different ways it can be established with relative ease.
In addition, we will also consider its several applications such as the particular case of Euler’s identity, the exponential form of complex numbers, alternate definitions of key functions, and alternate proofs of de Moivre’s theorem and trigonometric additive identities.
Lee, Sarah. 2025. “Applying Euler’s Formula to Real Problems.” Number Analytics // Super Easy Data Analysis Tool for Research. Accessed June 10. https://www.numberanalytics.com/blog/applying-euler-formula-real-problems.
Euler’s Formula, one of the most beautiful and profound equations in mathematics, bridges complex numbers with trigonometry. Originating from the work of the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, this formula has become a cornerstone of modern algebra, calculus, and engineering. In the context of Algebra II, it provides elegant solutions to complex equations, enriching our understanding of the relationship between exponential and trigonometric functions.
In this article, we’ll explore how Euler’s Formula is applied to real problems. We will examine its theoretical foundations before delving into practical applications including the conversion of complex numbers between rectangular and polar forms, solving complex equations, creating visualizations using the complex plane, and even integrating trigonometric functions. With step-by-step examples and practice problems, this guide is designed to boost your confidence and improve your problem-solving skills.
“Euler’s Formula.” 2024. GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/eulers-formula/.
Euler’s formula holds a prominent place in the field of mathematics. It aids in establishing the essential link between trigonometric functions and complex exponential functions. It is a crucial formula used for solving complicated exponential functions. It is also known as Euler’s identity. It has a lot of applications in complex analysis and is used to find the number of vertices and faces of a polyhedral.
Notes
Taylor Series
“Taylor Series: Theorem, Proof, Formula & Applications in Engineering.” 2025. GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/taylor-series/.
A Taylor series represents a function as an infinite sum of terms, calculated from the values of its derivatives at a single point.
- Taylor series is a powerful mathematical tool used to approximate complex functions with an infinite sum of terms derived from the function’s derivatives at a single point.
- Each successive term in the Taylor series expansion has a larger exponent or a higher degree term than the preceding term.
- We take the sum of the initial four, and five terms to find the approximate value of the function but we can always take more terms to get the precise value of the function.
- Finding approximate values of functions helps in many fields like Machine Learning, Economics, Physics, Medical and Biomedical Engineering.
Maclaurin Series
“Maclaurin Series.” 2020. GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. June 16. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/maclaurin-series/.
Prerequisite – Taylor theorem and Taylor series We know that formula for expansion of Taylor series is written as:

Now if we put a = 0 in this formula we will get the formula for expansion of Maclaurin series. Thus Maclaurin series expansion can be given by the formula
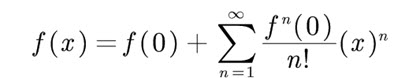
Interesting Facts about Euler’s number e
“Interesting Facts about Euler’s Number ‘e.’” 2024. GeeksforGeeks. GeeksforGeeks. October 28. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/interesting-facts-about-euler-s-number-e/.
Euler number is an irrational number, meaning its decimal form goes on forever without repeating. Like the well-known number π (pi), e has many fascinating mathematical qualities.
Mathematically, e is expressed as:

Euler’s Formula
Euler’s Number

φ, e and π
Videos
Euler’s Identity is one of the most popular math equations. In this video you’ll learn what it really means.
What does it mean to compute eπi?
Key analogies:
* Multiplication as a transformation
* Exponential growth as a continuous change
* Imaginary numbers as rotation
* Exponential, imaginary growth as continuous rotation
* Radians as distance traveled around the circle
Combining the analogies, you can see e^ix as a rotation around the circle, equivalent to
cos(x) + i*sin(x), which is the position in a “grid system”.
⭐ I suggest that you read the entire reference. Other references can be read in their entirety but I leave that up to you.
The featured image on this page is from the Zane Stirling Blog.